Search Books
For Better Search Results Only Write Subject OR Topic Name Like ( Math , Physics , Database , Algorithm ).
Slides - Week 5 , 6 , 7 and 8 - Fundamentals of Thermal Sciences
Description: Slide 1: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics
Slide 2: Work is the energy transfer associated with a force acting through a distance.
Slide 3: P1= 10 kPa
Slide 4: Moving boundary Work/ Thermal Work
Slide 5: Polytropic Process
Slide 6: ENERGY BALANCE FOR CLOSED SYSTEMS
Slide 7: Specific Heat
Slide 8: For an ideal gas at constant pressure, it takes more heat to achieve the same temperature
Slide 9: Enthalpy which is defined to be the sum of the
Slide 10: Heat capacity ratio
Slide 11: Chapter 7
Slide 12: Second Law of Thermodynamics
Slide 13: Second Law of Thermodynamics
Slide 14: These devices operate in a mechanical cycle but not in a thermodynamic cycle since the working
Slide 15: An external-combustion engine
Slide 16: The fraction of the heat input that is converted to net work output is a measure of the
Slide 17: The amount of heat supplied to the gas is greater than the work done since part of the
Slide 18: The Clausius statement
Slide 19: The transfer of heat from a low-temperature medium to a high-temperature one requires
Slide 20: Second Law of Thermodynamics
Slide 21: 21
Slide 22: 22
Slide 23: Entropy
Slide 24: With entropy of a closed system naturally increasing, this means
Slide 25: The change in entropy is given by
Slide 26: As we know that Work done by or on a system
Slide 27: Entropy Change of an Incompressible Substance
Slide 28: If Specific heat is Function of Temperature
Slide 29: Thermal process on T-s and p-v diagrams
Slide 30: Isentropic process is an idealized process that is both adiabatic and reversible.
Slide 31: A reversible process is defined as a process that can be reversed without leaving any
Slide 32: A process can be reversible only when its
Slide 33: Irreversibilities
Slide 34: Carnot Cycle and Internal Combustion Engines
Slide 35: 35
Slide 36: On a PV diagram the area under the process curve represents the
Slide 37: Carnot Heat Engine
Slide 38: Why Carnot Cycle is ideal
Slide 39: The hypothetical heat engine that operates on the reversible Carnot
Slide 40: [No Text Found]
Slide 41: Energy has quality as well as quantity.
Slide 42: Internal Combustion Engines
Slide 43: Bore: The bore of the cylinder is its diameter.
Slide 44: In a four-stroke internal combustion engine, the piston executes four distinct strokes
Slide 45: Air-Standard Otto Cycle
Slide 46: On T-s diagram , Area 2–3–a–b–2 represents heat added per unit of mass and area 1–
Slide 47: Efficiency of Air-Standard Otto Cycle
Slide 48: It is advantageous for internal combustion engines to have high compression ratios
Slide 49: [No Text Found]
Slide 50: ADVANTAGES OF 4 STROKE ENGINE :-
Slide 51: ADVANTAGES OF 2 STROKE ENGINE :-
Slide 52: Air-Standard Diesel Cycle
Slide 53: Process 1 to 2 is isentropic compression of the
Slide 54: Air-Standard Diesel Cycle
Slide 55: Efficiency of Air-Standard Diesel Cycle
Slide 56: Combustion is smooth and well propagating in
Slide 57: [No Text Found]
Slide 58: Gas turbines are one of the most widely-used power generating technologies.
Slide 59: The open Cycle GT: This is an engine in which
Slide 60: Work done by Turbine=
Please Login / Signup to Continue Download Study Material
Login to Continue Download
Uniwaly does not host or upload any files including books, notes, past papers, or other educational materials. All content is provided through publicly available links from third-party websites such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and other file-sharing platforms. We respect copyright laws and recommend users to only download content that is freely available or shared with permission. If you believe any file violates copyright, please contact us immediately for review.
More Study Materials

Understand & Survival - Lonely Planet

Vegetable Gardening for Dummies

حلال و حرام

Lonely Planet Guide
Lab Graphs - Book 1 EDC 1.1 Microsoft Excel File - Electric Devices

Elementary Visual School Arts
DC Power Supply Circuits 2 pdsprj File
29G2024

Oral Anatomy, Histology and Embryology by G R Holland & Bernard J Moxham

Download Dive Guide to the Philippines

Digital Signal Processing - Principles , Algorithms and Applications Proakis & Dimitris G. Manolakis

My kids can : making math accessible to all learners, K–5

Advances in Political Economy - Department of Political Science
138G2024

The Physics of Wall Street by James Owen Weatherall
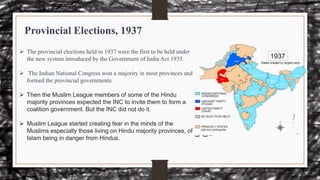
Provincials of Elections 1937
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUIT THEORY By ROBERT BOYLESTAD LOUIS NASHELSKY
31J2023
Thermodynamics : An Engineering Approach By Cengel , Yunus
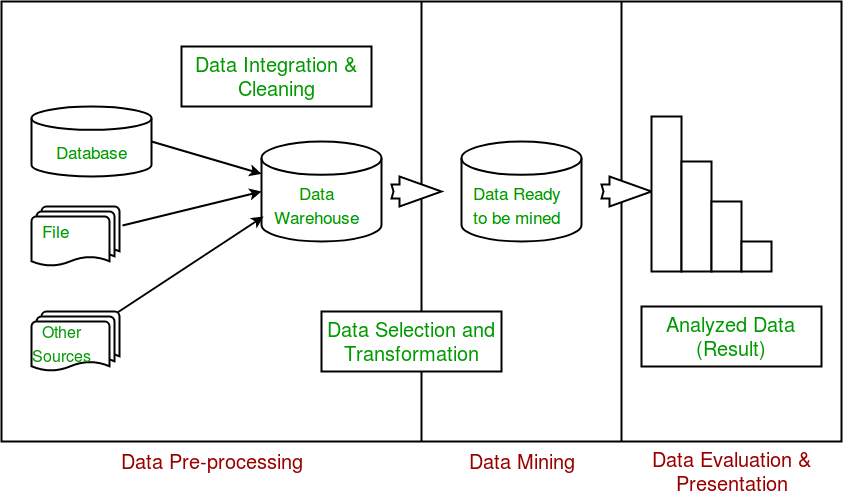
Lecture 2 - Data Mining on What Kind of Data? - Data Mining
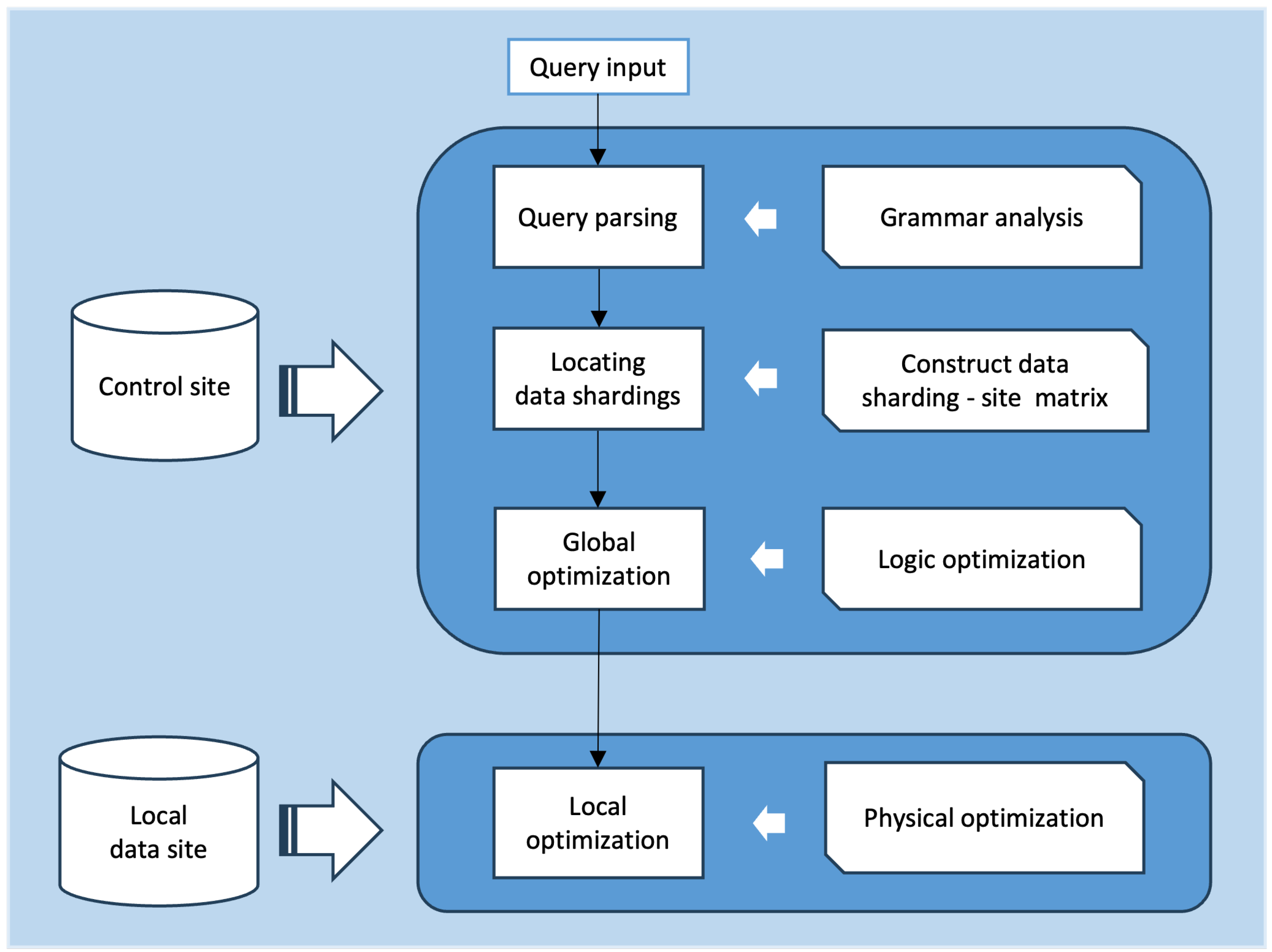
Lecture 11 - Query Optimization - Distributed Database Design
Chapter 2 : Electronic Devices & Circuits By Robert L. Boylestad Louis Nashelsky
Data Structure and Algorithms
Write a Program that inputs a number in main function and passes the number to a function. The function displays factorial of that number.
38H2024
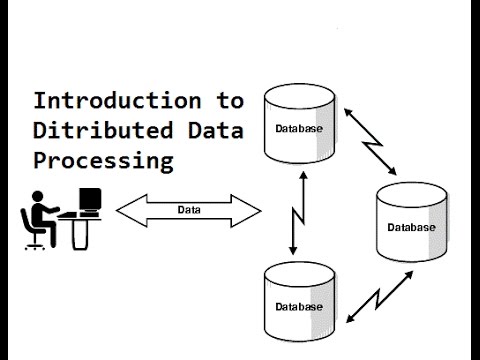
Lecture 1 - Distributed Database and Distributed Data Processing - Distributed Database Design

Politics: The Basics, 4th Edition

Communication Skills

Aalmi Malumat
54J2024
Display Number on Screen - Assembly Language Program
Structures - Method of Sections - Engineering Statics
32H2024
Lab Manuals - Experiment - Half Wave Rectifier

COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE
Fundamentals Of Electric Circuits 10th Edition
Introduction to Particle Physics
Equilibrium conditions in 2 dimensions - Engineering Statics

chemistry experiments for children

Barack H. Obama: the unauthorized biography